TM 5-3820-233-35/2
tween the commutator bars or other causes which would
(2)
Refer to figure 103 and disassemble
prevent good contact between the brushes and
the starter.
commutator.
e.
Cleaning.
(f)
Low no-load speed and low
current draw indicate a high internal resistance due to
(1) The drive, armature and fields should
poor connections, defective leads, dirty commutator and
not be cleaned in any degreasing tank, or with grease
causes listed under (e).
dissolving solvents, since these would dissolve the
(g) High free speed and high
lubricant in the dive and damage the insulation in the
current draw indicate shorted fields.
armature and field coils. All parts except the drive
should be cleaned with petroleum spirits and a brush.
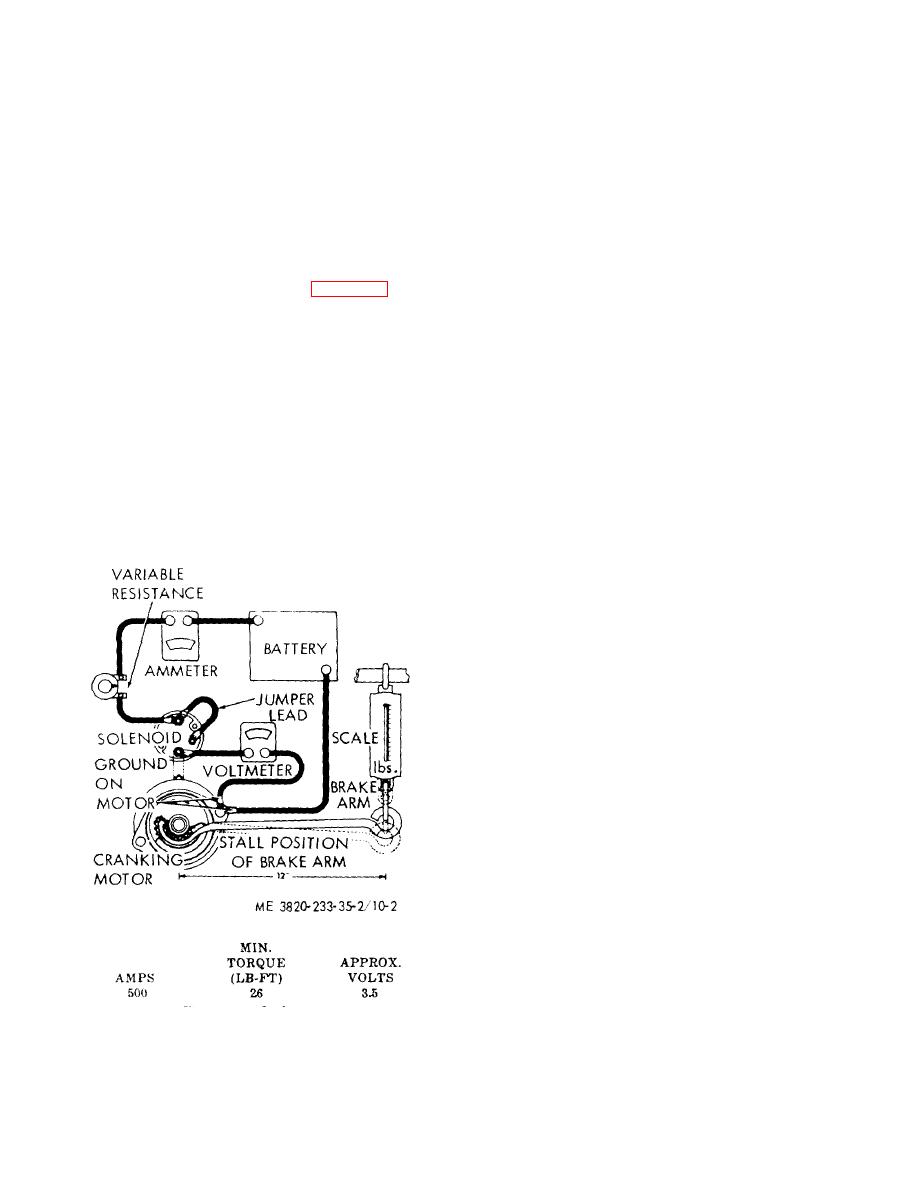
(3) Lock-Torque Test (fig. 10-2). The
The drive can be wiped with a clean cloth.
lock-torque test requires the equipment illustrated. A
(2) If the commutator is dirty it may be
variable resistance with a high current capacity should
cleaned with No. 00 sandpaper.
be used. The cranking motor should be SECURELY
mounted and a brake arm hooked to the drive. When
Caution
specified current is applied, the torque can be computed
Never use emery cloth to clean
from the reading on the scale. A one foot brake arm
commutator.
will directly indicate footpound. If the torque is low, the
motor must be disassembled for further tests and repair.
f.
Inspection and Repair.
(1) Inspect housings and frames for
d.
Disassembly.
cracks and distortion. Inspect threads in tapped holes
for damage. Replace defective parts.
(1) Scribe marks across drive housing,
(2) Inspect sleeve bearings for wear.
fever housing, frame and end bell to facilitate
Replace bearing if defective. Check for looseness in
reassembly in the correct relationship.
housing or end bell.
Replace worn or defective
bearings. If new bearing is loose in bore, replace
housing or end bell.
(3) Inspect wicks for tests, fraying, or
wear. Replace if defective.
(4) Turn down commutator if grooved or
out of round. Undercut mica to a depth of 0.025 to
0.032 inch below surface of commutator. Do not widen
slots when undercutting mica.
(5) Inspect drive pinion for broken or
badly worn teeth. Inspect clutch splines for wear and
damage. Inspect shell for cracked or broken condition.
Check to make sure pinion will drive into one direction
and will slip in opposite direction. Replace drive clutch
if defective.
(6) Inspect shift lever, shaft, and solenoid
plunger for cracks or distortion. Replace defective
parts.
(7) Inspect bellows for tears, punctures,
and deterioration.
or other damage. Replace if defective.
(9) Inspect brushes for wear or damage.
If damaged, or worn excessively, replace them.
g.
Testing.
(1) To test armature for grounds or short,
refer to TM 5-764.
Figure 10-2. Lock test.
3-2


